Modules and Available Third Party Software
Jobs Environment Management
Modules
“Modules” makes it easier for users to run a standard or customized application and/or system environment. HPCC uses Lmod - an advanced module system that easily handles the MODULEPATH hierarchical problem common in UNIX based "modules" implementation. Application packages can be loaded and unloaded cleanly through the module system using modulefiles. This includes easily adding or removing directories to the PATH environment variable. Modulefiles for Library packages provide environment variables that specify where the library and header files can be found.
All the popular shells are supported: bash, ksh, csh, tcsh, zsh. LMOD is also available for perl and python. Modules is available on KARLE, PENZIAS, APPEL and SALK.
Modules - getting started
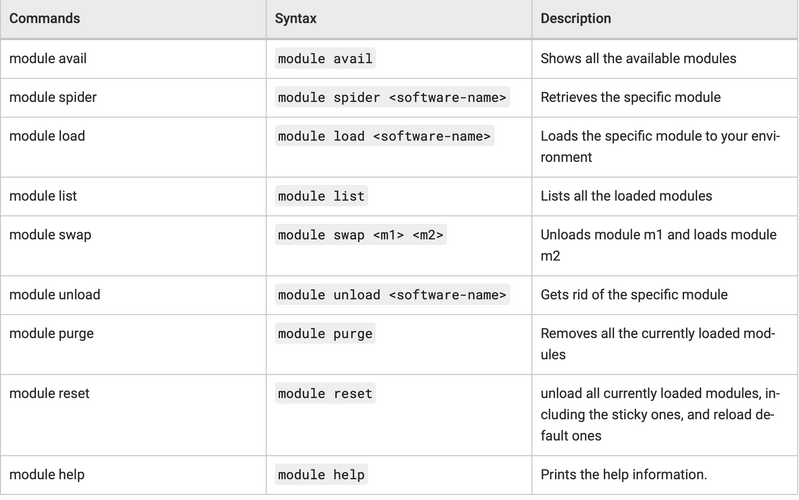
The basic module commands are listed below. Note that almost all applications have default version and several other versions. The default version is marked with (D). For example:
python/2.7.13_anaconda (D)
The default version can be loaded via its short name: . Non default version(s) require use of their full name. For example:
module load python
will load the default 2.7.13_anaconda version of python interpreter.To load non-default 3.7.6 the user must type
module load python/3.7.6_anaconda
The module load command can be used to load several application environments at once:
module load package1 package2 ...
For documentation on “Modules”:
man module
For help enter:
module help
To see a list of currently loaded “Modules” run:
module list
To see a complete list of all modules available on the system run:
module avail
To show content of a module enter:
module show <module_name>
To change from one application to another ( example. default versions of gnu and intel compiler):
module swap gcc intel
To go back to an initial set of modules:
module reset
Using LMOD commands
To get a list of all modules available
module spider
To get information about a specific module
module spider python
Modules for the advanced user
A “Modules” example for advanced users who need to change their environment.
The HPC Center supports a number of different compilers, libraries, and utilities. In addition, at any given time different versions of the software may be installed. “Modules” is employed to define a default environment, which generally satisfies the needs of most users and eliminates the need for the user to create the environment. From time to time, a user may have a specific requirement that differs from the default environment.
In this example, the user wishes to use a version of the NETCDF library on the HPC Center’s Cray Xe6 (SALK) that is compiled with the Portland Group, Inc. (PGI) compiler instead of the installed default version, which was compiled with the Cray compiler. The approach to do this is:
- • Run module list to see what modules are loaded by default.
- • Determine what modules should be unloaded.
- • Determine what modules should be loaded.
- • Add the needed modules, i.e., module load